

So in NPV we find the present value off all cash outflows i.e. Where N is the number of periods, n is a specific period, C is the cash flow for a particular period and r is the discount rate for each period.
The NPV calculation ends with the last cash flow. And future money is discounted by the interest rate you specify.Īssuming cash flows occur at the end of each period, an NPV with a 10% discount rate would divide the cash flow of period 1 by (1 + 10%) then add the cash flow in period 2 divided by (1 + 10%) ^2, etc. Basically, money today is worth more than money tomorrow.
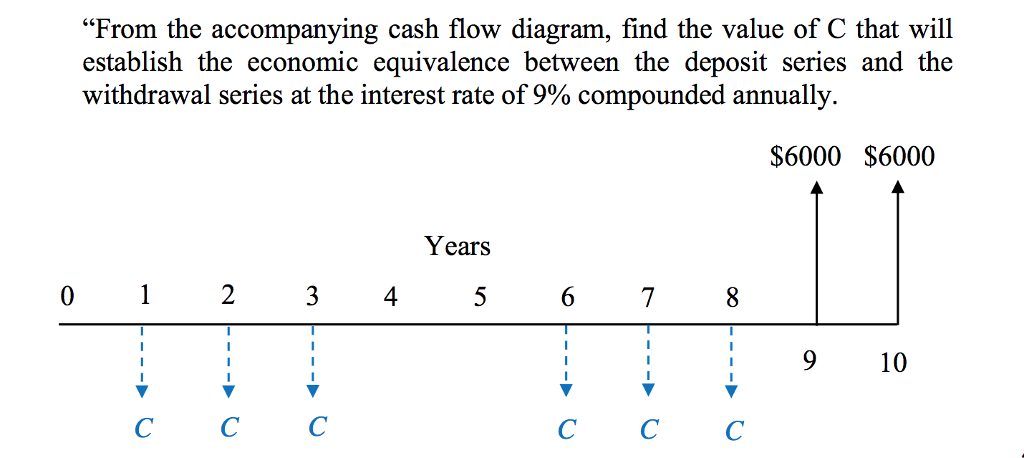
#ANNUAL WORTH IRREGULAR CASHFLOWS SERIES#
Net Present Value is the current value of a future series of payments and receipts and a way to measure the time value of money. XMIRR is the MIRR when periodicity between cash flows is not equal XIRR is the IRR when the periodicity between cash flows is not equal MIRR is the actual IRR when the reinvestment rate is not equal to IRR IRR is the rate of return at which NPV is zero or actual return of an investment. NPV is a number and all the others are rate of returns in percentage. These measures allow an investor to find out the rate of return he is earning on his investment. Payments is a specified collection of cash flows with corresponding dates, to which the discount will be applied.All NPV, IRR, MIRR, XIRR and XMIRR are used to analyze investments and to choose between 2 investments. XNPV: Use to determine the present value of an investment or annuity based on a series of irregularly spaced cash flows and at a discount interest rate. Guess is an estimate of the internal rate of return. Payments is a specified collection of cash flows with corresponding dates. XIRR: Use to determine the internal rate of return for an investment that is based on a series of irregularly spaced cash flows. This is commonly called the net present value.Ĭash-flow, cash-flow… is a specified series of one or more cash flows that may implicitly include a payment, present-value, and future-value. NPV: Use to determine the present value of a series of potentially irregular cash flows that occur at regular time intervals.
MIRR differs from IRR in that it permits positive and negative cash flows to be discounted at a different rate.įinance-rate and reinvest-rate are specific cases of periodic-rate. This is commonly called the modified internal rate of return. MIRR: Use to determine a periodic rate such that the net present value of a series of potentially irregular cash flows that occur at regular time intervals is equal to 0. This is commonly called the internal rate of return.įlows-range is a specified collection of cash flows that may implicitly include a payment, a present-value, and a future-value. IRR: Use to determine a periodic rate such that the net present value of a series of potentially irregular cash flows that occur at regular time intervals is equal to 0. Num-periods, payment, present-value, future-value, when-due, estimate RATE ( periodic-rate): Use to determine the periodic interest rate for a loan or annuity, based on the other factors such as the number of periods in the loan or annuity. Periodic-rate, num-periods, payment, future-value, when-due PV ( present-value): Use to determine the present value of a series of cash flows (what it is worth today), considering the other factors such as the interest rate. Periodic-rate, num-periods, present-value, future-value, when-due PMT ( payment): Use to determine the amount of the payment that would be required on a loan or received on an annuity, considering the other factors such as interest rate. Periodic-rate, payment, present-value, future-value, when-due NPER ( num-periods): Use to determine the number of periods it would take to repay a loan or the number of periods you might receive an annuity, considering the other factors such as the interest rate. Periodic-rate, num-periods, payment, present-value, when-due Functions that accept conditions and wildcards as argumentsįV ( future-value): Use to determine the future value of a series of cash flows (what it is worth at a future point in time), considering the other factors such as the interest rate.Tips for using double quotations in formulas.Review formula errors and best practices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
